
Calcium Carbonate
Process of Leavening •Leavening agents: -Also called leaveners. -Allow baked goods to rise. •Leavened baked goods: are lighter in. •Sources of calcium: calcium salts, such as calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate. Factors Affecting Yeast Fermentation 8. Amount of yeast. -More yeast means faster fermentation.

Calcium Carbonate Powder (E170) The Melbourne Food Depot, Melbourne
Food additives with strong water-absorbing capacity were patent protected, including calcium carbonate, calcium sulphate, diatomaceous earth and fruit peels. Table 1. Neutral fillers for chemical leavening, with patent priority date * Compound. Leavening acids like tartrates accelerated flour rancidity (Watts et al., 1949).

Calcium carbonate powder uncoated TLG 220 Thien Long (Vietnam
Calcium carbonate is a GRAS ingredient. Its use as a food additive is regulated by FDA under 21CFR582.1191. 4 . References. Erdogan, N., and Eken, H. A. (2016). Precipitated calcium carbonate production, synthesis and properties. Physiochemical Problems of Mineral Processing. 53 (2017), 57-68. How baking works-leavening agents.
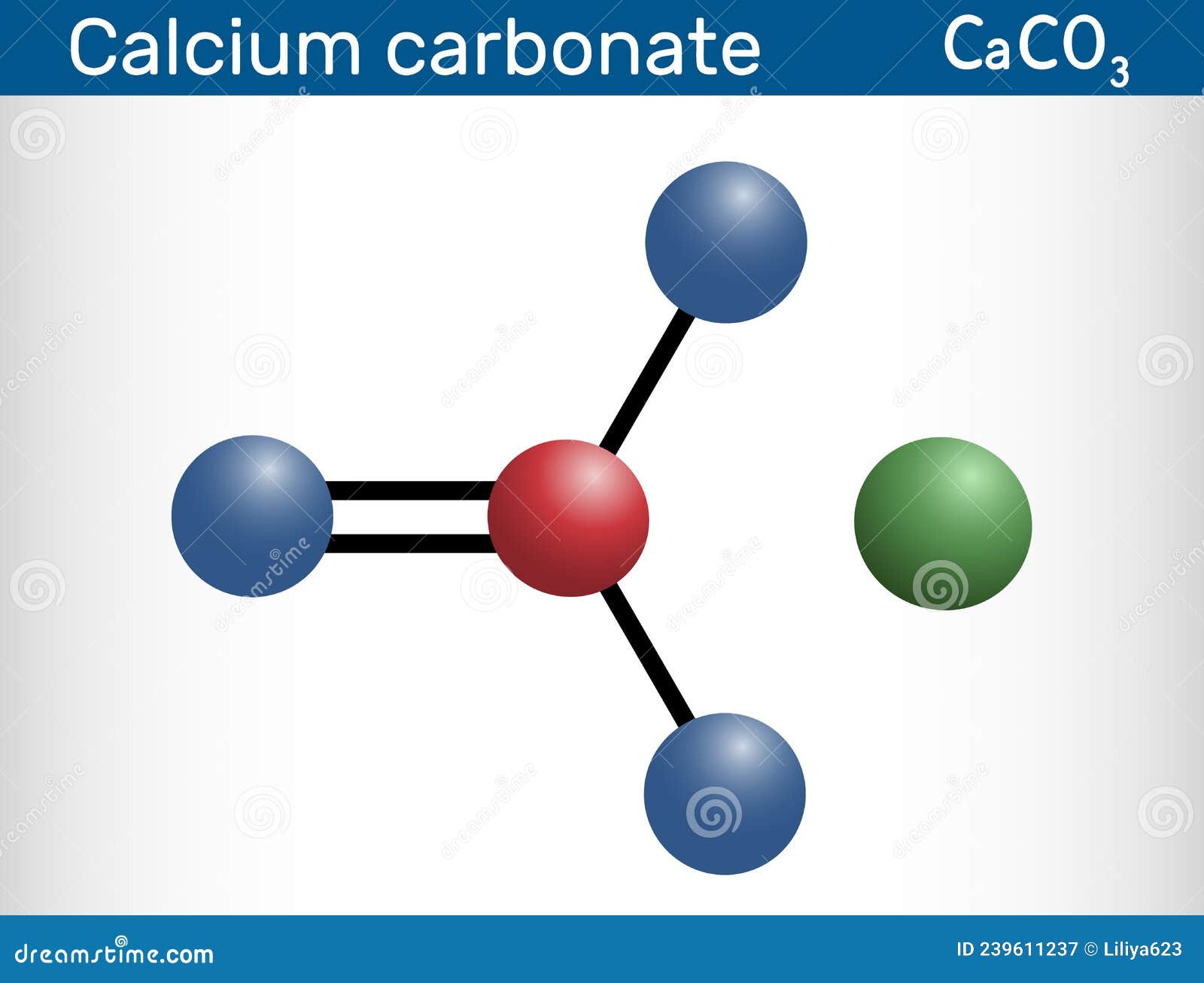
Calcium Carbonate Molecule. it is an Ionic Compound, the Carbonic Salt
Calcium carbonate, with its slower leavening action, creates a more tender and moist texture, which is ideal for cakes and quick breads. Beyond Baking: Other Uses. While both calcium carbonate and baking soda excel in the world of baking, they also have their own unique uses outside of the oven. Let's explore the versatile nature of these.

E170 Calcium Carbonate This Nutrition
calcium carbonate (CaCO3), chemical compound consisting of one atom of calcium, one of carbon, and three of oxygen that is the major constituent of limestone, marble, chalk, eggshells, bivalve shells, and corals. Calcium carbonate is either a white powder or a colorless crystal. When heated, it produces carbon dioxide and calcium oxide (also.

To Know Ground Calcium Carbonate from Six Aspects DASWELL
Calcium carbonate may cause serious side effects. Call your doctor at once if you have: little or no urinating; swelling, rapid weight gain; or. high levels of calcium in your blood-- nausea, vomiting, constipation, increased thirst or urination, muscle weakness, bone pain, confusion, lack of energy, or feeling tired.

OSTEOBLOC Applied Pharmaceutical Distribution Inc.
This, in turn, varies according to what you're baking. But the simplest way to think of it is that the leavening agent produces the gas, and the gas causes the dough or batter to rise. There are three main types of leavening agents: biological, chemical, and steam.

Calcium Carbonate 96.8 APC Pure
Abstract. There are many different leavening agents available to the baker. These include active dry yeast, sourdough starter, baking soda (sodium bicarbonate), baking powder (baking soda, calcium phosphate, and sodium aluminum sulfate), potash (potassium bicarbonate) or pearl ash, and bakers' ammonia (ammonia carbonate).

NEW Bubble & Bee Alkalizing Toothpaste LEMON Bubble and Bee Organic
Leavening Agents. Leaven is any agent that produces fermentation and causes dough to rise, by causing the formation of carbon dioxide gas to bubble into and spread throughout the dough. This is accomplished either chemically (as with baking soda) or biologically (as with yeast).

Calcium Carbonate Production
The calcium and aluminum cations in phosphate-based leavening acids provide more resiliency to cake products than the sodium cation in other phosphate-based leavening agents. Therefore, if resiliency is a property desired in a cake product, the formulator may choose a leavening system containing calcium and/or aluminum ions.

Understanding Calcium Carbonate Scale
Leavening agents produce gases via a reaction of a base like sodium bicarbonate and a weak organic acid, as lactic acid, citric acid, or tartaric acid.. In their model they account for 1) the presence of both a liquid and gas phase, 2) the hydration of CO2 into (bi)carbonate, and 3) the ionic strength of the dough (due to added salts.
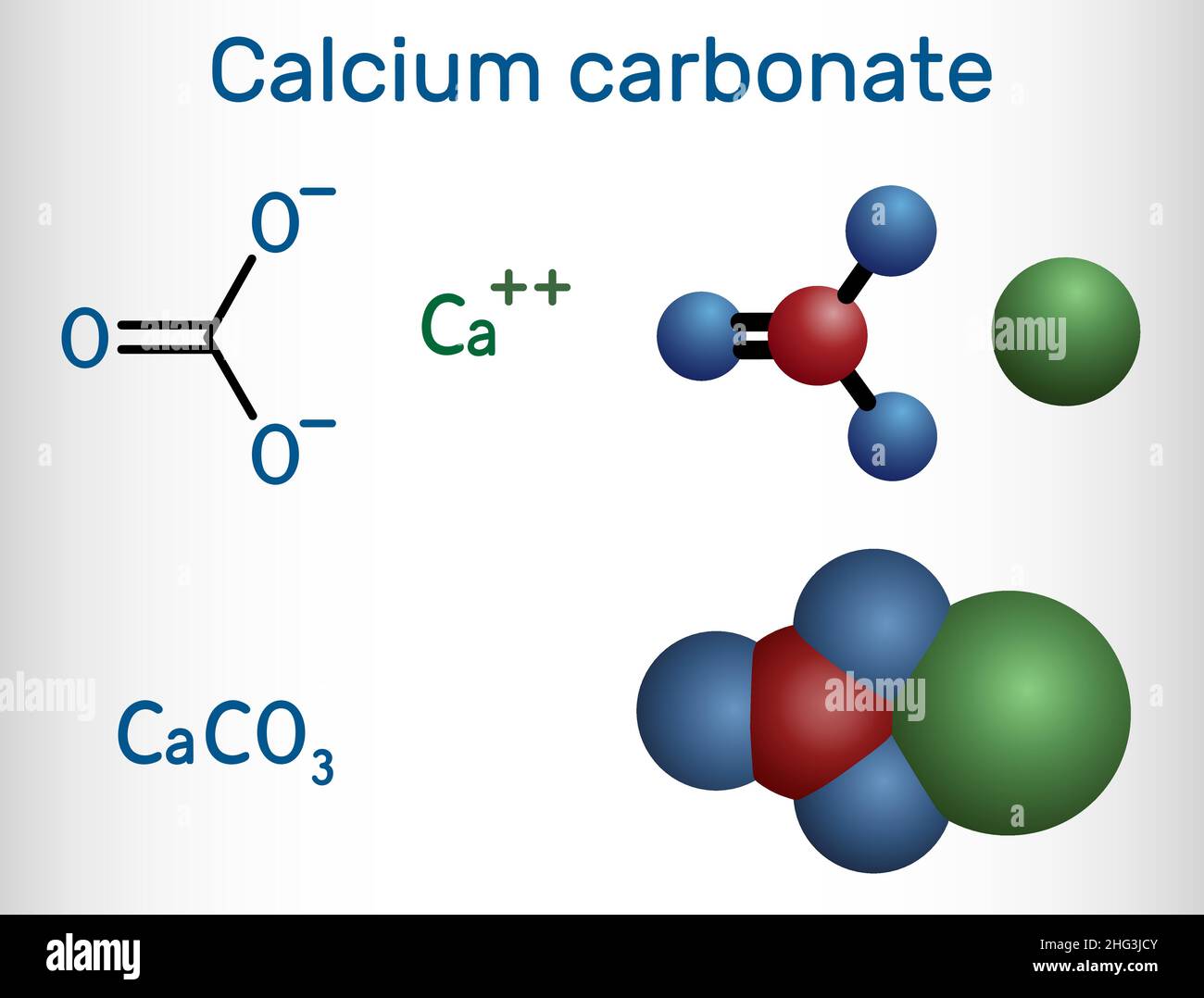
Calcium carbonate molecule. It is an ionic compound, the carbonic salt
leavening agent, substance causing expansion of doughs and batters by the release of gases within such mixtures, producing baked products with porous structure. Such agents include air, steam, yeast, baking powder, and baking soda. Air and steam. Leavening of baked foods with air is achieved by vigorous mixing that incorporates air bubbles, producing foam.

Amazingly Versatile Uses of Calcium Carbonate Science Struck
The prevalent baking acids in modern chemical leavening systems are sodium or calcium salts of ortho, pyro, and complex phosphoric acids. Baking soda determines the amount of carbon dioxide evolved, whereas the type of acid controls the speed of liberation. By far, the greatest use of leavening in the home is in preleavened mixes..

Green Calcite calcium carbonate CaCO3 Stock Photo Alamy
Calcium carbonate is a type of naturally occurring calcium salt that is often used as a food additive, an antacid, a phosphate binder, or a dietary supplement. As a pharmaceutical product, it can.

Full carbonate chemistry at the site of calcification in a tropical coral
Below are leavening agents and products found in a variety of foods that must be used up or removed by the Feast of Unleavened Bread along with a list of products often confused as leavening. Leavening Agents and Products (please note that this is not an all encompassing list) Yeast. Baker's yeast. Active dried yeast. Baking powder. Baking soda.
Calcium Carbonate Sujata Nutri Pharma limestone
Calcium carbonate is an inorganic salt primarily used to manage and treat low calcium conditions, GERD, CKD, and other indicated conditions. Calcium carbonate is classified as a calcium supplement, antacid, and phosphate binder. This activity outlines the significant indications, actions, and contraindications for calcium carbonate as a valuable agent in treating osteoporosis, hypothyroidism.